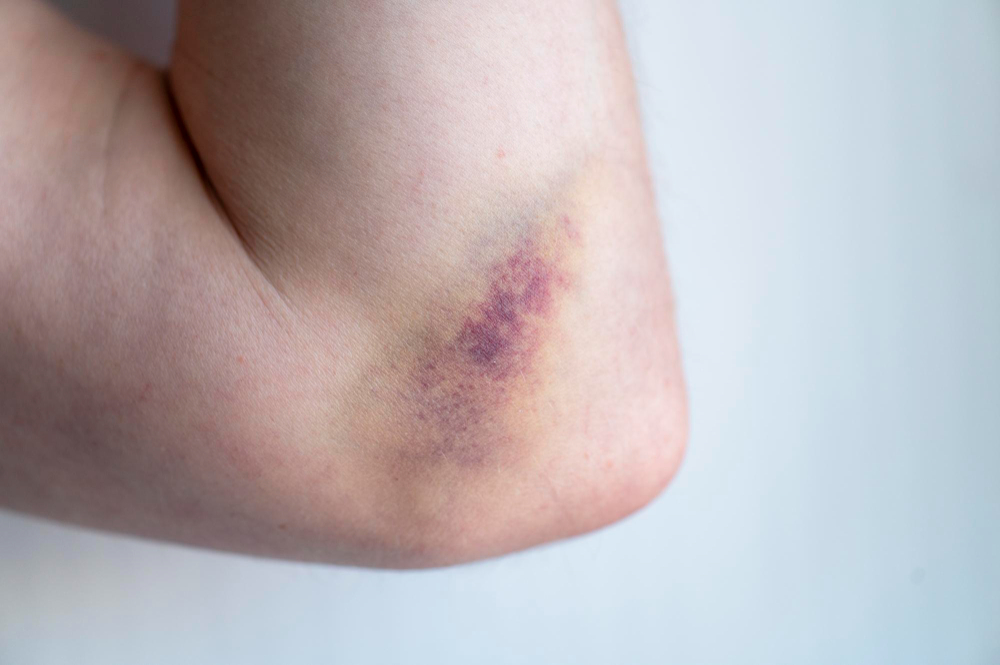
Introduction
Thrombocytopenia means you have fewer platelets in your blood than normal. Platelets help your blood clot and stop bleeding. Because of this, low platelets can lead to easy bruising or bleeding. Understanding thrombocytopenia causes and treatments is important for your health and safety. This guide will explain what you need to know in simple terms.
Causes of Thrombocytopenia
There are many reasons why someone may have low platelets. Some causes are common, while others are rare. Knowing the cause helps doctors choose the right treatment for you.
Common Causes
Rare Causes
Sometimes, doctors cannot find a clear cause. Even then, they can help manage your symptoms.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Many people with mild thrombocytopenia may not notice any symptoms. However, as platelet levels drop, signs may appear. For example, you might see:
If you notice these signs, you should talk to a doctor. Early care can prevent serious problems.
Diagnosis
Doctors use blood tests to check your platelet count. They may also ask about your health history and any medicines you take. Sometimes, more tests are needed to find the cause. For example, doctors may check your bone marrow or look for infections. Quick diagnosis helps start the right treatment.
Treatments for Thrombocytopenia
Treatment for low platelets depends on the cause and how low your platelet count is. In many cases, mild thrombocytopenia does not need treatment. But if your platelets are very low or you have bleeding, doctors may suggest:
Along with medical care, you can help manage thrombocytopenia by avoiding activities that may cause injury. Always follow your doctor’s advice for the best results.
Prevention Tips
While you cannot prevent all cases, you can lower your risk in some ways. For instance:
These steps can help keep your platelets at a healthy level.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice unusual bruising, bleeding, or red spots on your skin, you should see a doctor soon. Also, if you have a known risk for low platelets, regular check-ups are important. Early care can prevent serious problems and help you stay healthy.
Conclusion
Thrombocytopenia causes and treatments can seem complex, but simple steps can help you manage your health. If you have symptoms or concerns, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Sources: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), World Health Organization (WHO)